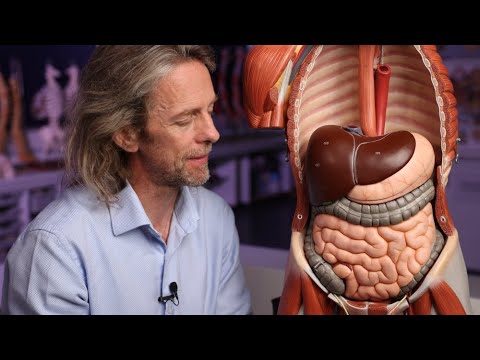
Introduction to the Gallbladder and Digestive Health
When people think about digestion, they usually picture the stomach. However, understanding How the Gallbladder Supports Fat Digestion and Overall Digestive System Function is essential for complete digestive health. The gallbladder may be small, but its impact is powerful.
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. Though modest in size, it plays a critical role in digesting fats and supporting nutrient absorption. Without it, your body can still function—but digestion may not be as efficient.
At Local MD, primary care professionals emphasize preventive care and patient education. Understanding your digestive system empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
Understanding the Digestive System: A Coordinated Process
Digestion isn’t random—it’s a carefully coordinated process involving multiple organs.
The Role of the Liver in Bile Production
The liver produces bile, a greenish-yellow fluid essential for breaking down fats. This bile contains bile salts, cholesterol, and waste products. However, bile production alone isn’t enough. It must be stored and delivered efficiently—and that’s where the gallbladder comes in.
How the Gallbladder Stores and Concentrates Bile
The gallbladder acts as a storage reservoir. It concentrates bile by removing excess water, making it stronger and more effective. When you eat fatty foods, the gallbladder contracts and releases bile into the small intestine.
This precise timing ensures fats are digested properly. Without this mechanism, fat digestion becomes slower and less efficient.
What Is Bile and Why Is It Essential for Fat Digestion?
Bile is not an enzyme, yet it plays a fundamental role in digestion.
Bile Salts and Their Impact on Fat Breakdown
Bile salts break large fat globules into smaller droplets—a process called emulsification. This increases the surface area for enzymes to work.
Emulsification: The Science Behind Fat Absorption
Imagine trying to wash greasy dishes without soap. It wouldn’t work well. Bile acts like soap in your digestive system. It allows fats to mix with water, making absorption possible.
This process is vital for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins such as:
-
Vitamin A
-
Vitamin D
-
Vitamin E
-
Vitamin K
Without proper bile release, these nutrients may not be absorbed efficiently.
Step-by-Step Process of Fat Digestion in the Body
Understanding How the Gallbladder Supports Fat Digestion and Overall Digestive System Function requires looking at the entire digestive pathway.
From Mouth to Stomach
Fat digestion begins in the mouth but minimally. The stomach continues mechanical breakdown, but significant fat digestion does not occur here.
Small Intestine: The Main Site of Fat Absorption
The small intestine is where the magic happens. When fatty food enters:
-
Hormones signal the gallbladder to contract.
-
Concentrated bile is released.
-
Pancreatic enzymes break down fats into fatty acids.
-
Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream.
This coordination ensures your body gains energy from fats efficiently.
How the Gallbladder Supports Overall Digestive System Function
While fat digestion is the primary function, the gallbladder indirectly supports the entire digestive system.
Interaction with Pancreatic Enzymes
The pancreas releases lipase, an enzyme that digests fats. However, lipase works best when bile has already emulsified fats.
This teamwork ensures optimal digestion.
Nutrient Absorption and Energy Production
Fats are a dense energy source. Efficient digestion means better:
-
Energy levels
-
Hormonal balance
-
Cell membrane integrity
-
Brain function
Thus, understanding How the Gallbladder Supports Fat Digestion and Overall Digestive System Function helps explain its broader role in overall health.
Common Gallbladder Disorders and Their Effects
Gallbladder problems are common but manageable.
Gallstones and Inflammation
Gallstones form when bile hardens. They can cause:
-
Abdominal pain
-
Nausea
-
Indigestion
-
Infection
If untreated, inflammation (cholecystitis) may occur.
Life After Gallbladder Removal
People can live without a gallbladder. However, bile flows continuously into the intestine rather than being stored. Some individuals may experience:
-
Mild diarrhea
-
Fat intolerance
-
Bloating
Dietary adjustments often help manage symptoms.
Lifestyle Habits That Support Gallbladder Health
Preventive care matters. Consider these tips:
-
Maintain a healthy weight
-
Avoid rapid weight loss
-
Eat balanced meals with healthy fats
-
Stay hydrated
-
Exercise regularly
Small, consistent changes can make a big difference.
When to See a Primary Care Provider
You should consult a provider if you experience:
-
Persistent upper right abdominal pain
-
Fever with digestive symptoms
-
Yellowing of skin (jaundice)
-
Chronic indigestion
At Local MD, healthcare providers prioritize patient-centered care and early diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the gallbladder actually do?
It stores and concentrates bile to help digest fats efficiently.
Can I digest fats without a gallbladder?
Yes, but digestion may be less efficient.
What foods stress the gallbladder?
High-fat, fried, and heavily processed foods.
Are gallstones dangerous?
They can be if untreated. Medical evaluation is important.
Does everyone with gallstones need surgery?
Not always. Treatment depends on symptoms.
How can I prevent gallbladder disease?
Maintain a balanced diet and stable weight.
Conclusion
Understanding How the Gallbladder Supports Fat Digestion and Overall Digestive System Function reveals how interconnected the digestive system truly is. Though small, the gallbladder plays a powerful role in energy production, nutrient absorption, and digestive efficiency.
By prioritizing preventive care, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking timely medical advice, you can protect your digestive health for years to come. At Local MD, informed patients are empowered patients—and that makes all the difference.