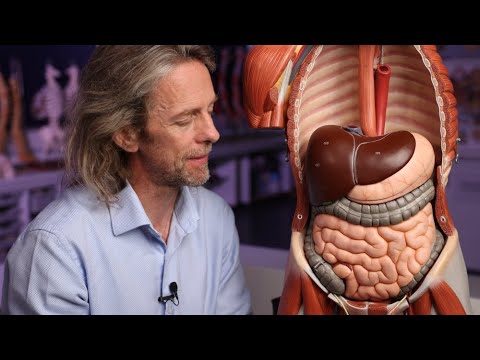
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, yet many people fail to recognize the warning signs until it’s too late. The human body often provides subtle clues that the heart is struggling, but these symptoms can be easily dismissed or attributed to other causes. Understanding which signs require immediate attention can mean the difference between early intervention and a life-threatening emergency.
The most critical heart disease symptoms that should never be ignored include chest pain or discomfort, severe shortness of breath, unexplained fatigue, irregular heartbeat, and sudden dizziness or fainting. However, heart disease symptoms extend far beyond these obvious warning signs. Many people experience more subtle indicators such as nausea, arm pain, or persistent coughing that may signal underlying heart problems.
Recognizing both the immediate and developing symptoms of heart disease empowers individuals to seek timely medical care. From understanding when chest discomfort warrants emergency attention to identifying circulation problems that develop gradually, knowing these warning signs can help prevent serious complications and potentially save lives.
Immediate Heart Disease Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
Certain heart disease symptoms demand immediate medical attention because they may indicate a heart attack or other life-threatening cardiac emergency. These critical warning signs include severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, radiating pain to the jaw or back, and sudden onset of cold sweats.
Chest Pain or Discomfort
Chest pain remains the most common sign of heart attack and should never be ignored. The pain typically feels like pressure, tightness, or squeezing in the center of the chest rather than a sharp, stabbing sensation.
Many people describe the feeling as an elephant sitting on their chest or a burning sensation. The discomfort usually lasts longer than a few minutes and may come and go.
Key characteristics of cardiac chest pain:
- Pressure or crushing sensation
- Located in the center of the chest
- Lasts more than 2-3 minutes
- May worsen with activity
If chest discomfort occurs with other symptoms like sweating or shortness of breath, this indicates heart problems requiring emergency care. Some individuals, particularly women, may experience a heart attack without typical chest pain.
Pain that worsens when touched or is very brief typically suggests non-cardiac causes. However, anyone experiencing persistent chest discomfort should seek immediate evaluation from a cardiologist or emergency medical services.
Shortness of Breath
Sudden or severe shortness of breath can indicate coronary artery disease or heart failure. This symptom may occur alone or alongside chest pain during a cardiac emergency.
Heart-related breathing difficulties often develop when the heart cannot pump blood effectively. Blood backs up into the lungs, causing fluid accumulation and making breathing difficult.
Warning signs include:
- Sudden onset of breathing problems
- Difficulty breathing while at rest
- Feeling like you cannot catch your breath
- Breathing problems with minimal exertion
People may experience shortness of breath during activities they previously completed without difficulty. This change in exercise tolerance represents a significant red flag for heart disease symptoms.
Emergency medical attention becomes necessary when breathing difficulties occur suddenly or worsen rapidly. The combination of shortness of breath with chest discomfort, dizziness, or sweating particularly suggests a heart attack.
Jaw, Neck, or Back Pain
Pain radiating from the chest to the jaw, neck, or back represents a classic heart attack symptom that people often overlook. This radiating pain typically begins in the chest area and spreads outward.
The pain usually starts in the chest and moves up into the throat, jaw, or down into the back. Some individuals experience mainly arm or jaw pain without significant chest discomfort.
Characteristics of cardiac-related radiating pain:
- Begins in chest area
- Spreads to left arm, jaw, neck, or back
- Occurs with other symptoms
- Feels like pressure rather than sharp pain
Women more commonly experience jaw or back pain as their primary heart attack symptom. These symptoms of heart problems require the same urgent attention as chest pain.
Isolated jaw or neck pain usually stems from muscular issues or other non-cardiac causes. However, when this pain accompanies chest pressure or breathing difficulties, it strongly suggests coronary artery disease complications.
Sudden Cold Sweats
Breaking into a cold sweat without obvious cause can signal a heart attack, especially when combined with other cardiac symptoms. This symptom represents the body’s stress response to decreased heart function.
Cold sweats differ from normal perspiration because they occur suddenly and feel clammy rather than warm. The sweating typically happens without physical exertion or hot environmental conditions.
Distinguishing features of cardiac sweating:
- Sudden onset
- Clammy, cold feeling
- No apparent trigger
- Accompanies other symptoms
When cold sweats occur with chest pain, shortness of breath, or nausea, this combination strongly indicates heart problems requiring immediate medical intervention. These symptoms together suggest the heart muscle is not receiving adequate blood supply.
People should call emergency services rather than driving themselves to the hospital when experiencing sudden cold sweats with other cardiac symptoms. Time becomes critical in treating heart attacks and preventing permanent heart muscle damage.
Subtle or Developing Warning Signs of Heart Trouble
Heart disease often develops gradually with symptoms that appear unrelated to heart trouble. These subtle signs can include extreme fatigue during routine activities, unexplained swelling in the lower extremities, and persistent digestive issues that may indicate underlying heart conditions.
Unexplained Fatigue
Extreme fatigue represents one of the most overlooked early signs of heart disease, particularly among women. When the heart struggles to pump blood effectively, the body receives less oxygen-rich blood to fuel daily activities.
This fatigue differs significantly from normal tiredness after a long day. Patients often describe sudden exhaustion when performing tasks they previously completed without difficulty.
Key indicators include:
- Breathlessness after climbing stairs
- Unusual tiredness after carrying groceries
- Need for frequent rest during routine activities
- Fatigue that doesn’t improve with adequate sleep
Heart failure causes this symptom because the weakened heart muscle cannot meet the body’s demands for oxygenated blood. The condition forces other organs to work harder, creating a cycle of increased fatigue.
Women experiencing heart trouble may notice this symptom weeks or even months before other obvious signs appear. Anyone at risk for heart disease should monitor significant changes in energy levels and discuss persistent fatigue with their healthcare provider.
Swelling in Ankles, Feet, or Legs
Edema in the lower extremities occurs when the heart cannot pump blood efficiently throughout the circulatory system. Blood begins to back up in the veins, causing fluid to accumulate in tissues.
This swelling typically starts in the ankles and feet before progressing upward to the legs. The symptom often worsens throughout the day and may improve slightly after elevation or rest.
Signs to monitor:
- Shoes feeling tighter than usual
- Socks leaving deep indentations
- Pitting when pressing on swollen areas
- Progressive swelling that doesn’t resolve overnight
Heart failure also affects kidney function, reducing the body’s ability to eliminate excess water and sodium. This creates additional fluid retention that compounds the swelling problem.
The edema may appear gradually over weeks or develop more rapidly during acute heart episodes. Patients should seek medical evaluation when swelling persists for several days or accompanies other heart trouble symptoms.
Persistent Nausea or Indigestion
Digestive symptoms frequently accompany heart conditions, especially in women experiencing cardiac events. The heart and digestive system share nerve pathways that can create misleading symptom presentations.
Nausea, heartburn, and stomach pain may occur during heart attacks or develop as chronic symptoms of heart disease. These signs often get dismissed as dietary issues or stress-related problems.
Warning patterns include:
- Nausea without apparent cause
- Heartburn unrelated to meals
- Stomach pain with chest discomfort
- Vomiting during periods of chest pressure
Heart trouble can trigger these digestive symptoms through reduced blood flow to abdominal organs. The vagus nerve, which connects the heart to the digestive tract, may transmit cardiac distress as gastrointestinal discomfort.
Patients at risk for heart disease should pay attention when digestive symptoms occur alongside fatigue, shortness of breath, or unusual sweating. These combinations may indicate developing heart conditions requiring immediate medical attention.
Heart Rhythm and Circulatory Symptoms That Signal Heart Disease
Heart palpitations, dizziness, and fainting episodes often indicate heart problems that require immediate medical evaluation. These cardiac symptoms may signal underlying arrhythmias or circulation issues that can lead to serious complications.
Heart Palpitations or Irregular Heartbeat
Heart palpitations feel like the heart is racing, skipping beats, or fluttering in the chest. An irregular heart rhythm can occur during stress or excitement, but persistent abnormal heart rhythm patterns may indicate heart disease.
Normal palpitations typically last only a few seconds. However, sustained irregular heartbeat episodes lasting several minutes require medical attention.
Warning signs that indicate heart problems:
- Palpitations accompanied by chest pain
- Shortness of breath during episodes
- Dizziness or fainting with irregular rhythm
- Frequent episodes throughout the day
Some people experience palpitations from caffeine, lack of sleep, or anxiety. These cases usually resolve when the trigger is removed.
Atrial fibrillation represents one serious condition causing irregular heart rhythms. This arrhythmia increases stroke risk and requires proper treatment.
Dizziness or Lightheadedness
Dizziness can result from many causes, but certain patterns may indicate heart disease. Cardiac-related dizziness occurs when the heart cannot pump blood effectively to the brain.
Standing up quickly sometimes causes brief lightheadedness. This normal response differs from persistent or recurring dizzy spells.
Cardiac dizziness characteristics:
- Occurs with chest discomfort
- Happens during physical activity
- Accompanied by shortness of breath
- Persists for several minutes
Blood pressure drops when the heart struggles to maintain adequate circulation. This creates the dizzy sensation as brain blood flow decreases.
Heart rhythm problems also trigger dizziness episodes. Both fast and slow abnormal heart rhythms can reduce blood flow to the brain.
Fainting or Loss of Consciousness
Fainting episodes may indicate heart problems requiring urgent evaluation. Cardiac causes of fainting include dangerous arrhythmias, heart valve problems, or blocked blood vessels.
Simple fainting from standing too long differs from cardiac-related episodes. Heart-related fainting often occurs without warning or during physical activity.
Emergency warning signs:
- Fainting during exercise
- No memory of feeling faint beforehand
- Chest pain before losing consciousness
- Family history of sudden cardiac death
Dangerous heart rhythms can cause sudden loss of consciousness. These episodes require immediate medical attention as they may signal life-threatening conditions.
Heart valve problems sometimes restrict blood flow enough to cause fainting. Structural heart defects can also trigger episodes during physical exertion.
People who faint should avoid driving until cleared by a cardiologist.
When and How to Take Action for Concerning Symptoms
Taking swift action when heart disease symptoms appear can be life-saving, especially for individuals with existing risk factors. Understanding when to seek immediate emergency care versus routine medical evaluation helps ensure appropriate treatment timing.
Recognizing Risk Factors and Family History
Individuals with specific risk factors face higher likelihood of developing heart disease and should treat symptoms more seriously. High blood pressure, diabetes, and elevated cholesterol significantly increase cardiovascular risk.
Age plays a crucial role, with men over 45 and women over 55 showing greater susceptibility. Family history of heart disease doubles the risk when immediate relatives experienced heart attacks or arterial disease before age 60.
Additional risk factors include:
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Obesity (BMI over 30)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Chronic stress
People with multiple risk factors should monitor symptoms closely. Even mild chest discomfort or unexplained fatigue warrants medical attention in high-risk individuals.
The American Heart Association emphasizes that risk factor awareness helps distinguish between normal physical sensations and potential warning signs requiring evaluation.
Seeking Timely Medical Evaluation
Call 911 immediately for severe chest pain lasting more than a few minutes, especially when accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea. Emergency situations require immediate intervention to restore blood flow and minimize heart muscle damage.
Symptoms requiring emergency care include:
- Crushing chest pain or pressure
- Pain radiating to arm, jaw, or back
- Severe difficulty breathing
- Loss of consciousness
- Cold sweats with chest discomfort
Schedule urgent medical appointments for persistent fatigue, irregular heartbeat, or swelling in legs and ankles. These symptoms may indicate the heart cannot pump blood effectively.
Healthcare providers use diagnostic tests like EKGs, blood tests, and imaging studies to evaluate heart health. Early detection allows for preventive treatments before conditions progress to heart attacks or heart failure.
Lifestyle Changes for Heart Health
Immediate lifestyle changes can significantly improve cardiovascular outcomes alongside medical treatment. Dietary modifications should focus on reducing saturated fats, sodium, and processed foods while increasing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle and improves circulation. The American Heart Association recommends 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly, including walking, swimming, or cycling.
Cholesterol management through diet and medication helps prevent arterial disease progression. High blood pressure control requires medication compliance, sodium restriction, and stress management techniques.
Diabetes management directly impacts heart health since elevated blood sugar damages blood vessels over time. Smoking cessation provides immediate cardiovascular benefits and reduces heart attack risk within one year.
Weight management reduces strain on the cardiovascular system and helps control other risk factors simultaneously.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding when heart symptoms require urgent attention can be lifesaving. The following questions address the most critical warning signs that indicate immediate medical evaluation is necessary.
What are the warning signs of a heart attack that demand immediate medical attention?
Chest pain that feels like pressure or squeezing, pain radiating to arms or jaw, cold sweats, nausea, and shortness of breath require calling emergency services immediately.
Can shortness of breath be indicative of a cardiac problem?
Yes, breathlessness during normal activities or at rest can signal heart failure, where blood backs up in the lungs due to poor heart pumping function.
How does chest pain relate to potential heart conditions?
Chest pain from heart problems typically feels like pressure, tightness, or squeezing that may spread to shoulders, arms, back, or jaw, indicating angina or blocked arteries.
What symptoms might suggest the onset of a stroke?
Sudden face drooping, arm weakness, speech difficulty, severe headache, vision changes, and dizziness signal stroke and require immediate emergency medical care.
Are there specific heart disease symptoms that are more common in women?
Women more often experience subtle symptoms like fatigue, nausea, back pain, jaw pain, and shortness of breath rather than classic chest pain during heart attacks.
How can dizziness or lightheadedness be linked to heart health issues?
Dizziness occurs when the brain receives insufficient blood flow due to blocked arteries, heart valve problems, or irregular heart rhythms affecting circulation.